项目仓库:https://github.com/Jason-xy/WuhuTakeOff.git
目标需求
1.模块单独运行
(1)串口能够输出调试信息。
(2)OLED可以在飞控PCB上显示实时参数。
(3)单片机可以读取GY-86传感器数据。
(4)单片机可以控制电机以不同转速转动。
(5)单片机可以捕获接收机信号。
2.模块联动
(1)OLED和串口可以同步输出各项参数。
(2)将GY-86实时数据作为调试信息输出。
(3)根据接收机信号来调整电机转速。
3.用户程序
(1)系统初始化。
(2)基础外设初始化。
(3)硬件模块初始化。
a.调试信息输出设备初始化。
b.电机初始化。
c.传感器初始化。
d.电机自动解锁。
e.接收机初始化。
f.参数显示界面绘制。
(4)后台程序:参数输出。
(5)前台程序:串口中断、TIM中断。
解决方案
硬件集成方案
硬件选型
**机械部分(略):**机架、电机、电调、电池。
飞控部分:
主控芯片:STM32F411CEU6
板型:最小系统板。裁剪多余模块,仅留下供系统运行的最小系统,体积小,自定义潜力大。
优点:Cortex-M4、128K SRAM、512K Flash、100MHz主频、以及丰富的外设接口和较小的体积。
方便在进一步迭代中运行操作系统,以及添加红外测距、WiFi图传等外设。
上位机通讯:WIFI-ESP8266
优点:数据传输距离远、速度快,可以接入互联网。
在进一步迭代中方便飞控实现长距离、大数据量上位机传输任务,实现远程OTA固件更新、远程PID参数一键调整,同时还可扩展为WIFI图传、串口接收机、一旦接入互联网即可实现真正意义上的远距离控制等丰富功能。
板载参数显示:0.96存I2C OLED小屏幕
优点:方便在飞控上直接获取实时数据,即便不连接上位机也可以初步了解飞控运行情况。
姿态传感器:GY-86
优点:麻雀虽小,五脏俱全。
接收机:FS-IA10B
优点:提供10通道数据传输,可以实现更多自定义功能。
遥控器:Jumper T18
优点:兼容性以及自定义程度最高的Open TX开源操作系统。
硬件连接
借助CubeMX快速规划。
如图所示:
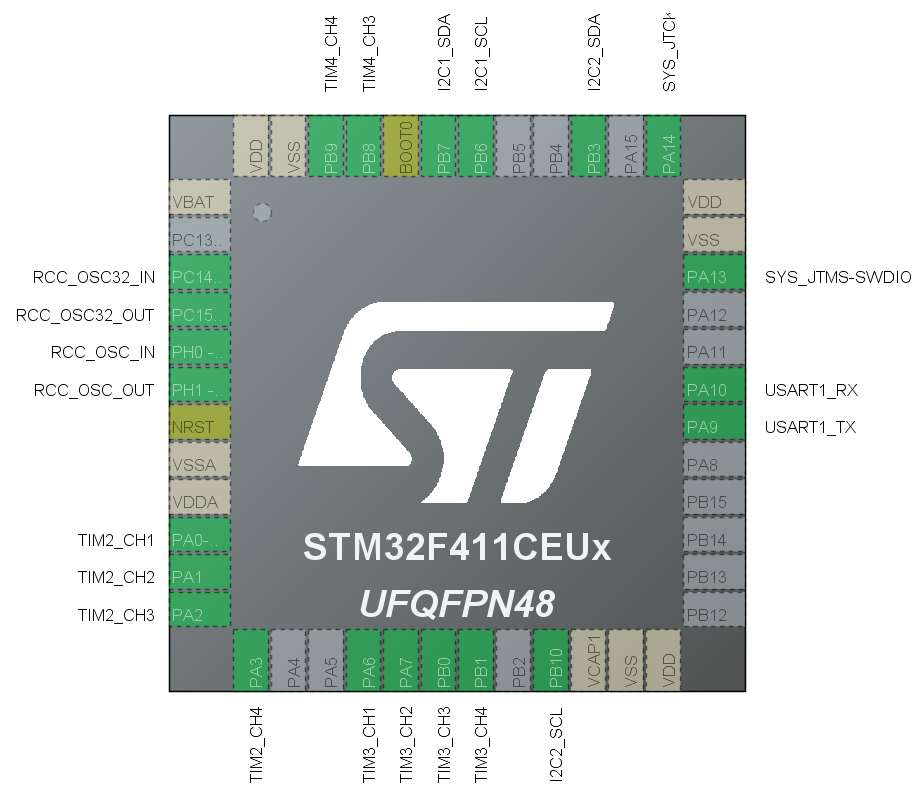
电路设计
原理图绘制(扩展板)

根据CubeMX生成引脚号进行连线即可。
可以考虑预留调试接口和其他外设的电源接口。
PCB绘制
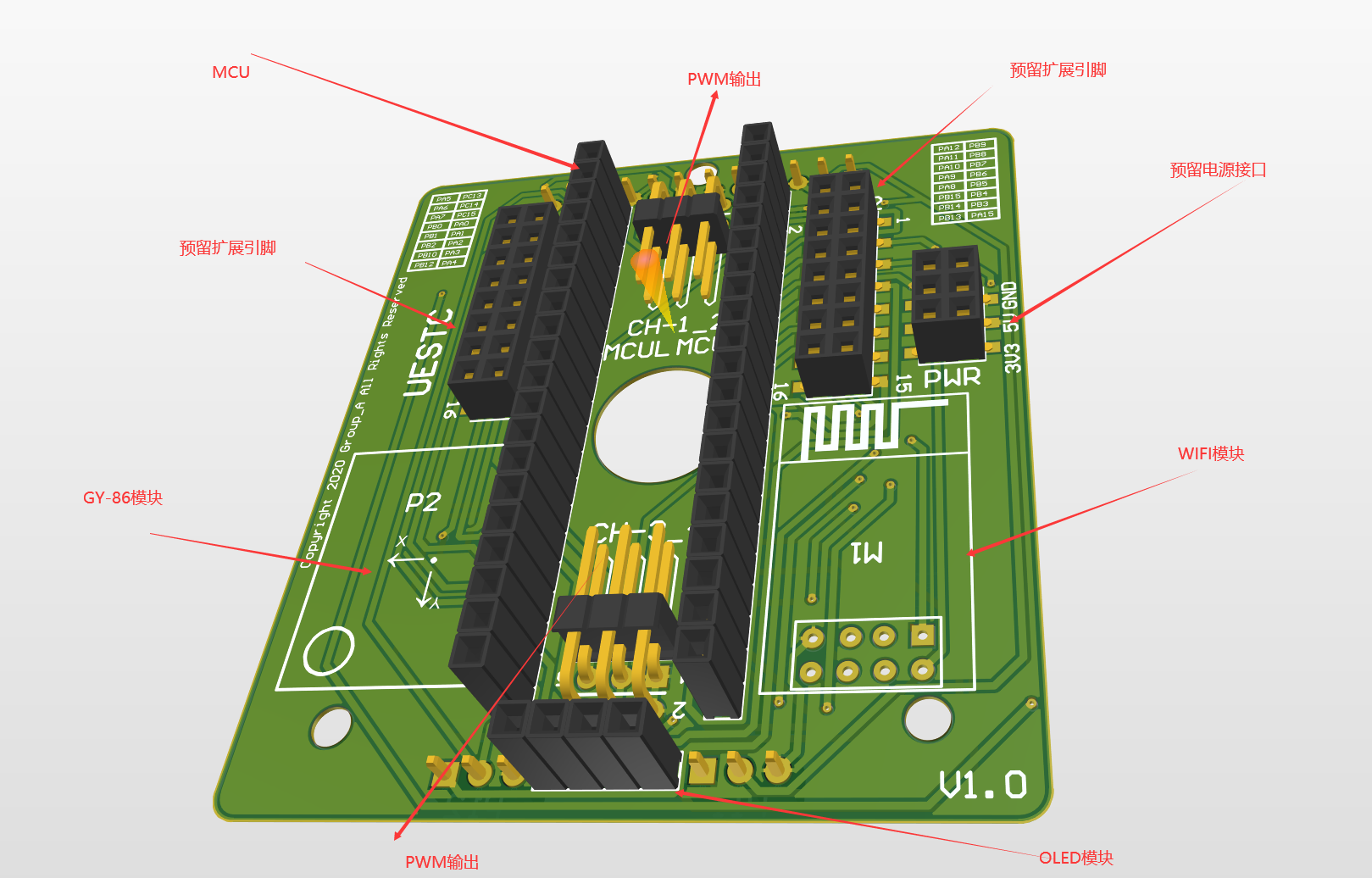
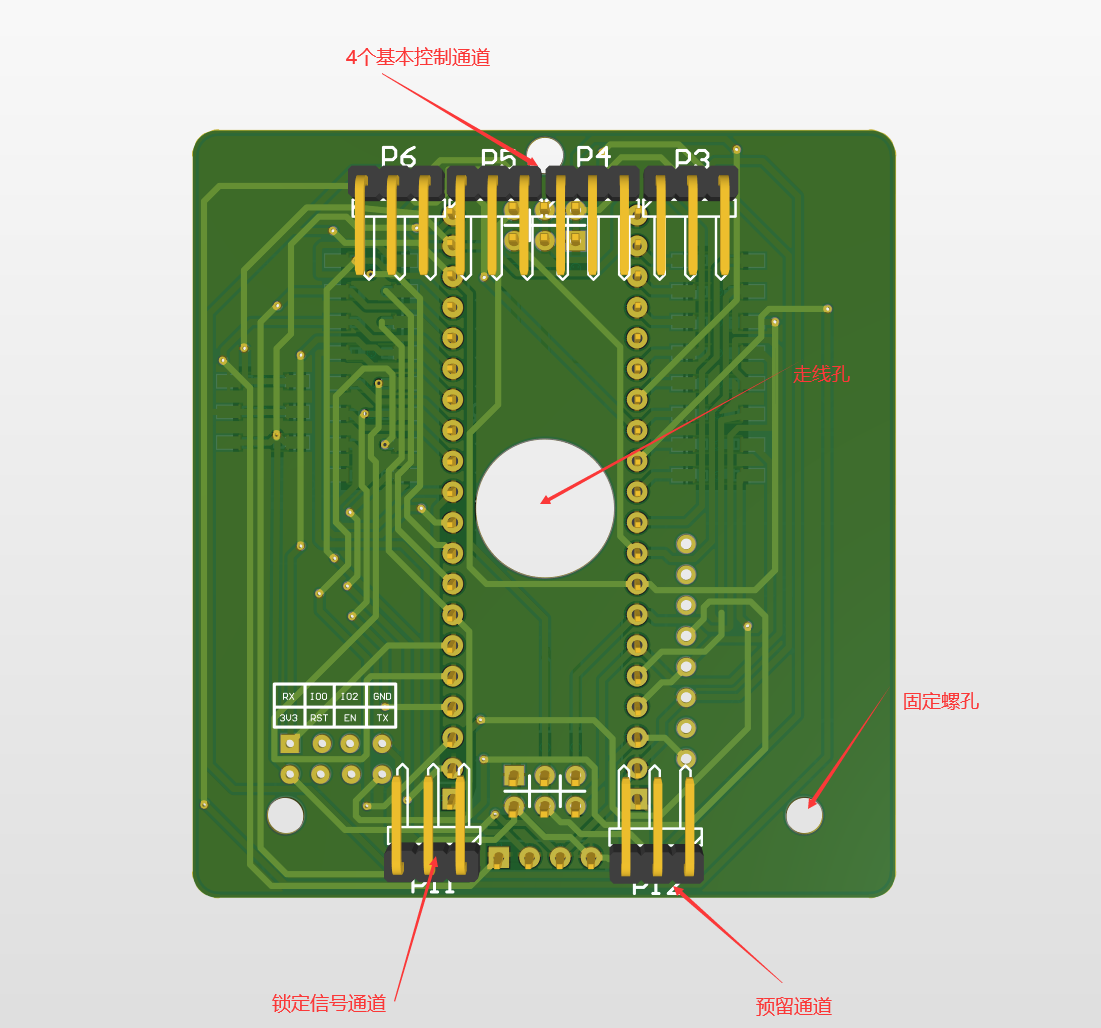
注意:
1.布局安排。
2.封装选择。
3.器件方向。
4.特殊网络规则。
原理图绘制(一体化半成品)
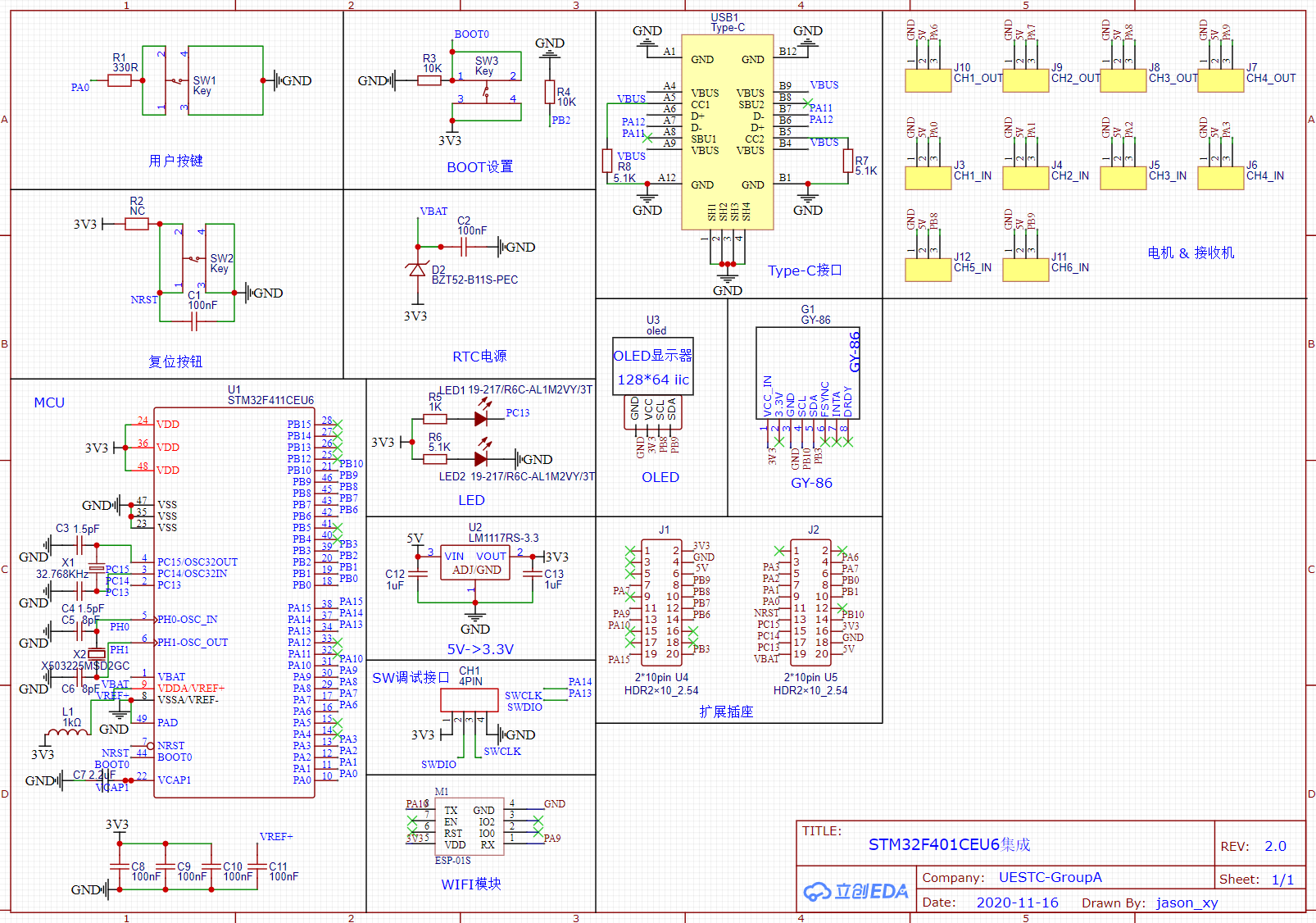
软件集成方案
STM32基于HAL库的的软件开发。
优点:效率高、逻辑性强、资料多、可移植性强。
缺点:复杂的代码量、极慢的编译速度、略微低下的效率、屏蔽硬件差异,需要挖掘库函数源码才能了解底层运作。
HAL库软件层级
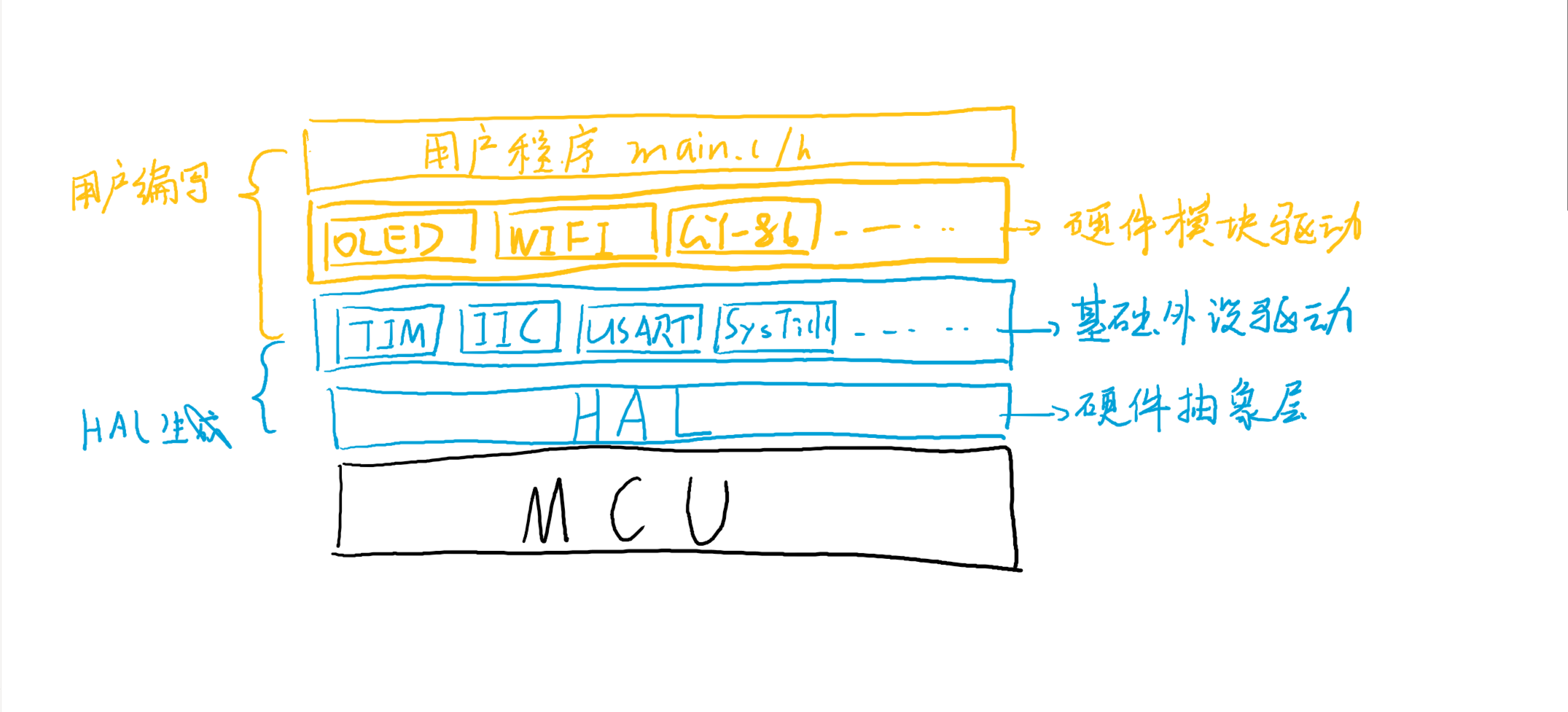
文件结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
| C:.
│ F411CEU6_V1.ioc
│ tree.txt
│
├─Core
│ ├─Inc
│ │ gpio.h
│ │ i2c.h
│ │ main.h
│ │ stm32f4xx_hal_conf.h
│ │ stm32f4xx_it.h
│ │ tim.h
│ │ usart.h
│ │
│ └─Src
│ gpio.c
│ i2c.c
│ main.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_msp.c
│ stm32f4xx_it.c
│ system_stm32f4xx.c
│ tim.c
│ usart.c
│
├─Drivers
│ |—CMSIS......
│ ├─HW
│ │ ├─inc
│ │ │ controller.h
│ │ │ esp8266.h
│ │ │ hmc5883l.h
│ │ │ motor.h
│ │ │ mpu6050.h
│ │ │ oled.h
│ │ │ oledfont.h
│ │ │
│ │ └─src
│ │ controller.c
│ │ esp8266.c
│ │ hmc5883l.c
│ │ motor.c
│ │ mpu6050.c
│ │ oled.c
│ │
│ └─STM32F4xx_HAL_Driver
│ ├─Inc
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_adc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_adc_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_can.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_cec.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_conf_template.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_cortex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_crc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_cryp.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_cryp_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_dac.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_dac_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_dcmi.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_dcmi_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_def.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_dfsdm.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_dma.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_dma2d.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_dma_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_dsi.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_eth.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_exti.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_flash.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_flash_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_flash_ramfunc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_fmpi2c.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_fmpi2c_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_fmpsmbus.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_gpio.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_gpio_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_hash.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_hash_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_hcd.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_i2c.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_i2c_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_i2s.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_i2s_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_irda.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_iwdg.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_lptim.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_ltdc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_ltdc_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_mmc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_nand.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_nor.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_pccard.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_pcd.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_pcd_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_pwr.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_pwr_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_qspi.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_rcc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_rcc_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_rng.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_rtc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_rtc_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_sai.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_sai_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_sd.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_sdram.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_smartcard.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_smbus.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_spdifrx.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_spi.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_sram.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_tim.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_tim_ex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_uart.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_usart.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_hal_wwdg.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_adc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_bus.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_cortex.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_crc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_dac.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_dma.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_dma2d.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_exti.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_fmc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_fmpi2c.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_fsmc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_gpio.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_i2c.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_iwdg.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_lptim.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_pwr.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_rcc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_rng.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_rtc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_sdmmc.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_spi.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_system.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_tim.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_usart.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_usb.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_utils.h
│ │ │ stm32f4xx_ll_wwdg.h
│ │ │ stm32_assert_template.h
│ │ │
│ │ └─Legacy
│ │ stm32f4xx_hal_can_legacy.h
│ │ stm32_hal_legacy.h
│ │
│ └─Src
│ stm32f4xx_hal.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_adc.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_adc_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_can.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_cec.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_cortex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_crc.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_cryp.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_cryp_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dac.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dac_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dcmi.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dcmi_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dfsdm.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dma.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dma2d.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dma_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dsi.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_eth.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_exti.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_flash.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_flash_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_flash_ramfunc.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_fmpi2c.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_fmpi2c_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_fmpsmbus.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_gpio.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_hash.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_hash_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_hcd.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_i2c.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_i2c_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_i2s.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_i2s_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_irda.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_iwdg.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_lptim.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_ltdc.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_ltdc_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_mmc.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_msp_template.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_nand.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_nor.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_pccard.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_pcd.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_pcd_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_pwr.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_pwr_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_qspi.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_rcc.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_rcc_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_rng.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_rtc.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_rtc_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_sai.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_sai_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_sd.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_sdram.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_smartcard.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_smbus.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_spdifrx.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_spi.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_sram.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_tim.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_timebase_rtc_alarm_template.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_timebase_rtc_wakeup_template.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_timebase_tim_template.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_tim_ex.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_uart.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_usart.c
│ stm32f4xx_hal_wwdg.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_adc.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_crc.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_dac.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_dma.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_dma2d.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_exti.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_fmc.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_fmpi2c.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_fsmc.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_gpio.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_i2c.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_lptim.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_pwr.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_rcc.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_rng.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_rtc.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_sdmmc.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_spi.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_tim.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_usart.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_usb.c
│ stm32f4xx_ll_utils.c
│
└─MDK-ARM
│ EventRecorderStub.scvd
│ F411CEU6_V1.uvguix.Jason
│ F411CEU6_V1.uvoptx
│ F411CEU6_V1.uvprojx
│ startup_stm32f411xe.lst
│ startup_stm32f411xe.s
│
├─DebugConfig
│ F411CEU6_V1_STM32F411CEUx.dbgconf
│
├─F411CEU6_V1
│ controller.crf
│ controller.d
│ controller.o
│ esp8266.crf
│ esp8266.d
│ esp8266.o
│ ExtDll.iex
│ F411CEU6_V1.axf
│ F411CEU6_V1.build_log.htm
│ F411CEU6_V1.hex
│ F411CEU6_V1.htm
│ F411CEU6_V1.lnp
│ F411CEU6_V1.map
│ F411CEU6_V1.sct
│ F411CEU6_V1_F411CEU6_V1.dep
│ gpio.crf
│ gpio.d
│ gpio.o
│ hmc5883l.crf
│ hmc5883l.d
│ hmc5883l.o
│ i2c.crf
│ i2c.d
│ i2c.o
│ main.crf
│ main.d
│ main.o
│ motor.crf
│ motor.d
│ motor.o
│ mpu6050.crf
│ mpu6050.d
│ mpu6050.o
│ oled.crf
│ oled.d
│ oled.o
│ startup_stm32f411xe.d
│ startup_stm32f411xe.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_cortex.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_cortex.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_cortex.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dma.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dma.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dma.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dma_ex.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dma_ex.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_dma_ex.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_exti.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_exti.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_exti.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_flash.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_flash.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_flash.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_flash_ex.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_flash_ex.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_flash_ex.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_flash_ramfunc.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_flash_ramfunc.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_flash_ramfunc.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_gpio.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_gpio.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_gpio.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_i2c.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_i2c.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_i2c.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_i2c_ex.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_i2c_ex.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_i2c_ex.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_msp.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_msp.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_msp.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_pwr.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_pwr.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_pwr.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_pwr_ex.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_pwr_ex.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_pwr_ex.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_rcc.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_rcc.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_rcc.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_rcc_ex.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_rcc_ex.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_rcc_ex.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_tim.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_tim.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_tim.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_tim_ex.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_tim_ex.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_tim_ex.o
│ stm32f4xx_hal_uart.crf
│ stm32f4xx_hal_uart.d
│ stm32f4xx_hal_uart.o
│ stm32f4xx_it.crf
│ stm32f4xx_it.d
│ stm32f4xx_it.o
│ system_stm32f4xx.crf
│ system_stm32f4xx.d
│ system_stm32f4xx.o
│ tim.crf
│ tim.d
│ tim.o
│ usart.crf
│ usart.d
│ usart.o
│
└─RTE
└─_F411CEU6_V1
RTE_Components.hCOPY
|
文件类型详解参考资料:Keil 项目/生成的各种文件类型(.AXF、.D、.crf、.exf)说明
HAL库用户文件
**主函数:**main.c/.h
MSP初始化: stm32f2xx_hal_msp_template.c ……
中断服务函数: stm32f2xx_it.c/.h
**硬件模块驱动:**mpu6050.c/.h ……
HAL库用户代码
HAL 库对底层进行了抽象,在此结构下,用户代码处理可分为三大部分:
1.句柄
在STM32的标准库中,假设我们要初始化一个外设(这里以USART为例)
我们首先要初始化他们的各个寄存器。在标准库中,这些操作都是利用固件库结构体变量+固件库Init函数实现的:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| USART_InitTypeDef USART_InitStructure;
USART_InitStructure.USART_BaudRate = bound;
USART_InitStructure.USART_WordLength = USART_WordLength_8b;
USART_InitStructure.USART_StopBits = USART_StopBits_1;
USART_InitStructure.USART_Parity = USART_Parity_No;
USART_InitStructure.USART_HardwareFlowControl = USART_HardwareFlowControl_None;
USART_InitStructure.USART_Mode = USART_Mode_Rx | USART_Mode_Tx;
USART_Init(USART3, &USART_InitStructure);
|
可以看到,要初始化一个串口,需要对六个位置进行赋值,然后引用Init函数,并且USART_InitStructure并不是一个全局结构体变量,而是只在函数内部的局部变量,初始化完成之后,USART_InitStructure就失去了作用。
而在HAL库中,同样是USART初始化结构体变量,我们要定义为全局变量。
1
| UART_HandleTypeDef UART1_Handler;
|
相关结构体成员:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| typedef struct
{
USART_TypeDef *Instance;
UART_InitTypeDef Init;
uint8_t *pTxBuffPtr;
uint16_t TxXferSize;
uint16_t TxXferCount;
uint8_t *pRxBuffPtr;
uint16_t RxXferSize;
uint16_t RxXferCount;
DMA_HandleTypeDef *hdmatx;
DMA_HandleTypeDef *hdmarx;
HAL_LockTypeDef Lock;
__IO HAL_UART_StateTypeDef State;
__IO uint32_t ErrorCode;
}UART_HandleTypeDef;COPY
|
我们发现,与标准库不同的是,该成员不仅包含了之前标准库就有的六个成员(波特率,数据格式等),还包含过采样、(发送或接收的)数据缓存、数据指针、串口 DMA 相关的变量、各种标志位等等要在整个项目流程中都要设置的各个成员。
该 UART1_Handler 就被称为串口的句柄
它被贯穿整个USART收发的流程,比如开启中断:
1
| uint8_t HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&UART1_Handler, (u8 *)aRxBuffer, RXBUFFERSIZE);COPY
|
比如后面要讲到的MSP与Callback回调函数:
1
2
| void HAL_UART_MspInit(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart);
void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart);COPY
|
在这些函数中,只需要调用初始化时定义的句柄UART1_Handler就好。
2.MSP函数
MCU Specific Package 单片机的具体方案
MSP是指和MCU相关的初始化:
1.一部分是与MCU无关的,协议层。
2.一部分是与MCU相关的,物理层。
举个例子:
1
2
3
| 我们要初始化一个串口,首先要设置和 MCU 无关的东西,例如波特率,奇偶校验,停止位等,这些参数设置和 MCU 没有任何关系,可以使用 STM32F1,也可以是 STM32F2/F3/F4/F7上的串口。
而一个串口设备它需要一个 MCU 来承载,例如用 STM32F4 来做承载,PA9 做为发送,PA10 做为接收,MSP 就是要初始化 STM32F4 的 PA9,PA10,配置这两个引脚。所以 HAL驱动方式的初始化流程就是:HAL_USART_Init()—>HAL_USART_MspInit() ,先初始化与 MCU无关的串口协议,再初始化与 MCU 相关的串口引脚。
在 STM32 的 HAL 驱动中HAL_PPP_MspInit()作为回调,被HAL_PPP_Init()函数所调用。当我们需要移植程序到 STM32F1平台的时候,我们只需要修改 HAL_PPP_MspInit 函数内容而不需要修改 HAL_PPP_Init 入口参数内容。COPY
|
**优点:**可移植性强。
**缺点:**增加代码量、增加代码嵌套层级。
同样,MSP函数又可以配合句柄,达到非常强的移植性:
1
| void HAL_UART_MspInit(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart);COPY
|
入口参数仅仅需要一个串口句柄,这样有能看出句柄的方便。
3.Callback函数
类似于MSP函数,Callback函数主要帮助用户应用层的代码编写。
还是以USART为例,在标准库中,串口触发中断了以后,我们要先在中断中判断是否是接收中断,然后读出数据,顺便清除中断标志位,然后再是对数据的处理,这样如果我们在一个中断函数中写这么多代码,就会显得很混乱:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| void USART3_IRQHandler(void)
{
uint8_t Res;
if(USART_GetITStatus(USART3, USART_IT_RXNE) != RESET)
{
Res =USART_ReceiveData(USART3);
}
}
} COPY
|
而在HAL库中,进入串口中断后,直接由HAL库中断函数进行托管:
1
2
3
4
5
| void USART1_IRQHandler(void)
{
HAL_UART_IRQHandler(&UART1_Handler);
}COPY
|
HAL_UART_IRQHandler这个函数完成了判断是哪个中断(接收?发送?或者其他?),然后读出数据,保存至缓存区,顺便清除中断标志位等等操作。
比如我提前设置了,串口每接收五个字节,我就要对这五个字节进行处理。
在一开始我定义了一个串口接收缓存区:
1
2
3
|
uint8_t aRxBuffer[RXBUFFERSIZE];COPY
|
在初始化中,我在句柄里设置好了缓存区的地址,缓存大小(五个字节)
1
2
3
4
|
huart->pRxBuffPtr = pData;
huart->RxXferSize = Size;
huart->RxXferCount = Size;
|
则在接收数据中,每接收完五个字节,HAL_UART_IRQHandler才会执行一次Callback函数:
1
| void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart);COPY
|
在这个Callback回调函数中,我们只需要对这接收到的五个字节(保存在aRxBuffer[]中)进行处理就好了,完全不用再去手动清除标志位等操作。
所以说Callback函数是一个应用层代码的函数,我们在一开始只设置句柄里面的各个参数,然后就等着HAL库把自己安排好的代码执行完毕就行了。
HAL库编程方式
在 HAL 库中对外设模型进行了统一,支持三种编程方式:
以IIC为例,三种编程模式对应的函数如下:
1、轮询模式/阻塞模式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| uint8_t HAL_I2C_Master_Transmit();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Master_Receive();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Slave_Transmit();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Slave_Receive();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Mem_Write();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Mem_Read();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_IsDeviceReady();COPY
|
2、中断模式
1
2
3
4
5
6
| uint8_t HAL_I2C_Master_Transmit_IT();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Master_Receive_IT();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Slave_Transmit_IT();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Slave_Receive_IT();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Mem_Write_IT();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Mem_Read_IT();COPY
|
3、DMA模式
1
2
3
4
5
6
| uint8_t HAL_I2C_Master_Transmit_DMA();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Master_Receive_DMA();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Slave_Transmit_DMA();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Slave_Receive_DMA();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Mem_Write_DMA();
uint8_t HAL_I2C_Mem_Read_DMA();COPY
|





